Download the Full April 2017 Issue PDF
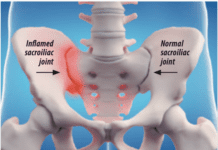
The key to treating gout is to lower the uric acid level in the blood until it is consistently less than 6 milli- grams (mg)/deciliter (dL). Chang- ing your diet can help, but even the strictest low-purine diet will only reduce uric acid levels by 1 mg/dL. If your level is 12 mg/dL, youll never get it low enough with diet alone, says Cleveland Clinic rheu- matologist Elisabeth Ray, MD.
Download the Full March 2017 Issue PDF
Participants, who had heart disease or were at increased risk for it, were randomly assigned to celecoxib (100 mg twice a day), ibuprofen (600 mg three times a day) or naproxen (375 mg twice a day), which they took for at least 18 months. There was no significant difference in the occurrence of heart attack, stroke or death between the three groups. One limitation of the study was the high number of people who dropped out. However, the drop-out rate was similar for all three groups, so I dont think it affects the overall conclusions, says Dr. Husni.
Download the Full February 2017 Issue PDF
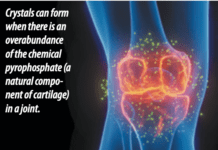
It seems logical that injecting HA into the joint should help relieve arthritis symptoms. But its unclear whether the synthetic HA gets incorporated into cartilage. Evidence about the effectiveness of injections is mixed, which has resulted in some disagreement among medical specialty societies about the role of this therapy. The American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons says the evidence does not currently support its use.
Download the Full January 2017 Issue PDF
If you have knee osteoarthritis and a meniscus tear, definitely try physical therapy. If youre getting progressively better, then stay with it for the complete course of sessions, says Dr. Spindler. People who dont make any progress should consider being evaluated for surgery. The surgery is called arthroscopic partial meniscectomy. With arthroscopic surgery, the surgeon makes small incisions through which a camera and surgical instruments are inserted.
Download the Full December 2016 Issue PDF
While they can be very effective, biologics have some drawbacks. Most of them must be taken by injection or intravenous infusion, and there are potential side effects, some of which can be serious. In most cases, the benefits will outweigh the risks, says Dr. Bunyard. But it may take some trial and error to find the right drug or combination of drugs that leads to remission or low disease activity without any unacceptable side effects.If you are on a regimen of drugs for rheumatoid arthritis and are still experiencing pain or dysfunction, it may be time to make a change. But Dr. Bunyard notes that increased pain and dysfunction may also stem from a different cause.
Download the Full November 2016 Issue PDF
Immobilizing the joint with a splint can help with pain and joint alignment. You can buy one in the drug store, but its better to have one custom made by an occupational therapist. If you buy a ready-made one, be sure it is specifically designed for the thumb (and not, for example, for the wrist). Some splints hold the joint in one position, while others allow for some movement. Your doctor or occupational therapist will help you determine which type of splint is most appropriate for you. Youll probably start by wearing the splint most of the time, and then gradually use it less frequently during the day but continue bracing while you sleep at night.
Download the Full October 2016 Issue PDF
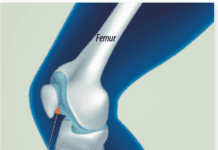
Hip resurfacing is an alternative that preserves more bone and may allow for greater mobility. With hip resurfacing, the socket part of the implant is the same as in the total joint replacement. But instead of inserting the stem and ball device into the femur, the surgeon reshapes the bone at the head of the femur and places a metal cap over it. A larger ball is used than in total joint replacement, which should make the joint more stable and less likely to dislocate. The neck of the thighbone and part of the head are preserved, which may make revision surgery or total hip replacement easier if needed later on.
Download the Full September 2016 Issue PDF
There are inherent difficulties in studying any treatments for osteoarthritis. First is the placebo effect. Some people will get better even when given an inactive treatment simply because they believe it will work.It is also tricky to evaluate any treatment for osteoarthritis because symptoms do not always steadily worsen. Instead, pain tends to come and go. It may not be clearly evident whether an improvement was the result of a treatment or the natural ebbing and flowing of symptoms.
Download the Full August 2016 Issue PDF
If the pain doesnt reflect the anatomical problem, how can your doctor know whats behind it? It starts with a good history and a physical examination, Dr. Murray says. Certain clues can point a diagnosis away from the knees and toward the hips. If the knee has good range of motion and no tenderness but the hip has poor range of motion, then youre tipped off that maybe this is somebody who has a hip problem and not a knee problem, says Dr. Murray. An X-ray should confirm the diagnosis by revealing joint erosion and cartilage loss in the hip and intact joints in the knees.
Download the Full July 2016 Issue PDF
Theres no conclusive evidence to guide a decision about glucosamine and chondroitin. The GAIT study did find that they are not harmful, and many people choose to try them. The dosages in the GAIT study were 1,500 mg a day of glucosamine and 1,200 mg a day of chondroitin. Dr. Husni tells her patients to try it for three months. If you dont notice a difference in symptoms such as pain or stiffness, dont waste your money, she says.
Download the Full June 2016 Issue PDF
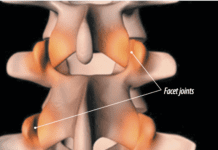
Posture can be difficult to correct. If you always hold your head slightly forward or hunch over, youre putting added stress on the joints and disks in the upper spine. But because your body has become accustomed to this position, it can feel strange to straighten up into correct posture. However, maintaining good posture becomes easier the longer you do it.
Download the Full May 2016 Issue PDF
For people with osteoarthritis in the shoulder, the wearing down of cartilage at the joint over time causes pain and stiffness. If oral medications fail to adequately ease pain, the next step often is corticosteroid injections into the joint to reduce inflammation. These can help many people with shoulder arthritis. But over time, they can become less effective.